• The State has around 52.38 lakh MSMEs which is around 11.55% of the total number of MSMEs in Indiain 2015-16.
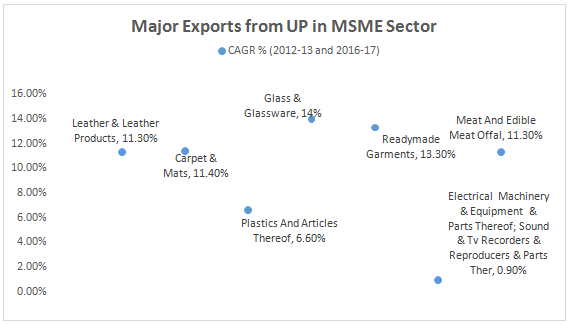
• With the second highest number of MSME units in the country, Uttar Pradesh today is a leading exporter of MSME products in categories like handicrafts, engineering goods, carpets, readymade garments, leather products etc.
| Industries |
No. Of Units |
Employment |
Investment (INR In Crores) |
| Food Products |
52,963 |
5,231.30 |
2,93,505 |
| Beverages, Toba. & Toba. Product |
563 |
108.73 |
3,043 |
| Cotton Textiles |
8,004 |
675.44 |
49,274 |
| Wool,Silk & Synthetic Fibre Textile |
7,250 |
670.64 |
52,871 |
| Jute,Hemp & Mesta Textiles |
1,352 |
168.01 |
4,810 |
| Hosiery & Garments |
24,359 |
1,967.29 |
1,84,084 |
| Wood Products |
7,692 |
810.53 |
44,467 |
| Paper Products & Printing |
3,643 |
786.99 |
26,344 |
| Leather Products |
4,991 |
982.32 |
62,352 |
| Rubber & Plastic Products |
3,144 |
1,266.93 |
35,052 |
| Chemical & Chemical Products |
3,174 |
910.39 |
33,645 |
| Non-Metallic Mineral Products |
2,103 |
477.80 |
19,269 |
| Basic Metal Industries |
1,673 |
420.17 |
14,446 |
| Metal Products |
13,270 |
2,076.75 |
1,05,221 |
| Machinery & Part Except Electrical |
3,987 |
1,141.20 |
51,186 |
| Electrical Machinery & Apparatus |
3,179 |
825.88 |
40,068 |
| Transport Equipment& Parts |
361 |
692.05 3,463 |
3,463 |
| Miscellaneous Mfg. |
1,59,774 |
14,566.38 |
7,81,510 |
| Repairing & Servicing Industries |
2,59,041 |
14296.20 |
1020415 |
| TOTAL |
560523 |
48075.01 |
2825025 |
Major sub-sectors in the state[2013-14 to 2017-18 (upto Sep,2017)]
Major MSME Clusters in the State -
Benefit of naturally existing clusters and gradually developed clusters like
- • Pottery cluster at Khurja,
- • Perfume & Essential Oil at Kannauj
- • Power loom cluster at Jhansi
- • Sheet work at Hathras
- • Power loom at Gorakhpur
- • Chemicals, Mechanical Equipment and Packing Material at Ghaziabad
- • Glass Products at Firozabad
- • Power loom at Banda
- • Power loom and Leather Products at Mau
- • Carpet cluster Bhadohi,
- • Leather goods and Cotton Hosiery at Kanpur
- • Sports goods and Scissors cluster at Meerut
- • Silk cluster Varanasi
- • Leather Footwear and mechanical engineering equipment cluster at Agra
- • Brass and silver handicraft cluster of Moradabad
- • Locks & hardware cluster of Aligarh
- • Wood work and Rice Mills cluster of Saharanpur
Key Investment Enablers
i. Human Resource availability –
- • With a total population of more than 200 Million, Uttar Pradesh boasts of a labour force of over 70 Million of which over 40 million are non-agricultural labour force
- • State has 4thhighest number of Engineering colleges, and 3rd highest no. of Colleges in India, followed by,2nd highest no of ITIs/ITCs, 3rd highest no of Polytechnics, and 3rd highest no of Business Schools in India.
- • Total 36 universities, 3104 colleges,1500 ITIs/ITCs, 197 business schools and 320 engineering colleges
- • UP accounts for about 10.1 % of the total National Highway (NH) network
- • 47 National Highways connect it with 9 neighbouring states and other parts of India
- • Largest railway network in the country spanning over 8,763 Km
- • 6 Domestic Airports at Agra, Allahabad, Gorakhpur, Kanpur, Lucknow and Varanasi and 1 international airport at Lucknow
- • Considerable share of the Western Corridor running between Delhi & Mumbai and Eastern Corridor running between Ludhiana and Kolkata set to revolutionise the logistics infrastructure and industrial corridors in the state
Key growth drivers
a. Indigenisation - With the advent of Make in India and enhanced focus on locally manufactured products, there is huge opportunity for investments and outputs by large players and their MSME vendors to indigenise and/or enable import substitution particularly adapting to research and development, innovation and global technologies.
b. Government Procurement policy and procurement by large domestic and foreign industries - A favourable procurement policy complemented by the huge industrial base in the state supports MSME vendors to grow their business in the state.
Policy Framework under Uttar Pradesh Industrial Investment and Employment Promotion Policy (IIEP) 2017
- • Incentives linked to employment generation and regional distribution.
- • Structural reforms for ease of doing business and industrial security.
- • Infrastructure support – by way of developing industrial parks, open access power, green measures, etc.
- • Institutional strengthening – by setting up State Investment Promotion Board (SIPB), Single Window Department, Make in UP.
- • Attractive fiscal incentives – in order to attract investments and ushering competitiveness.
- • Participative, forward looking and adapting policy framework – aiming to usher policy consistency.
Key growth drivers
Electronics
- • Electronic Systems Design and Manufacturing including semiconductor design, electronic components design and hi-tech manufacturing.
- • Electronic components with focus on making components for electronic products customised for the Indian market
- • Strategic electronics, with the Government of India keen to encourage domestic manufacturing of products needed by the armed forces
- • Low-cost consumer electronics, consumer durables
- • Nanoelectronics and microelectronics
Telecom
- • Domestic manufacturing of telecom networking equipment, including routers and switches.
- • Next generation Software-defined Networking equipment
- • Mobile Customer Data Analytics, services oriented towards analytical solutions
- • Manufacture of low-cost mobile phones, handsets and devices
- • Manufacture of Base Transceiver Station equipment
- • Development of Value-added Services
- • Over-the-top (OTT) service providers of innovative services and content to mobile subscribers
IT/ITes
- • Cloud computing
- • Social media and mobility
- • Data analytics services
- • E-governance
- • Mobile apps and software development
- • Software automation
- • Information Technology Cities – Noida, Lucknow, Kanpur, Agra & Allahabad.
Media
- • Manufacture of Set-Top Boxes (STB) for Direct-to-Home service providers
- • Digital screens in tier-2 and 3 cities
- • Digital Media, new forms of content delivery for media companies
Healthcare
- • Providing affordable healthcare, especially in rural areas
- • Low cost medical devices, which can be used in rural areas
- • Medical consumables like surgical gloves, scrubs, syringes etc
- • Low cost surgical procedures to reduce the cost of healthcare
- • Medical tourism
- • Diagnostic labs
Pharmaceuticals
- • Generics and API manufacturing
- • Contract research
- • Nutraceuticals and nutracosmetics
Biotechnology
- • Domestic manufacturing of diagnostic kits, reagents and consumables used in testing.
- • Focus on vaccine exports to developed countries
- • Providing bio-informatics related solutions
- • Leveraging the bio-similar opportunity Recombinant products
- • Agri produce
- • Hybrid seeds also represent new business opportunities based on yield improvement
Automotive
- • Automotive electronics
- • Manufacturing automotive components - Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers to OEMs
- • Applied electronics
- • Rubber and chemicals supply to the tyre
Transport & Logistics
- • Green supply chain
- • Reusable packaging material
- • Technology intensive transport and logistics management
- • Fleet Management System
Industrial Manufacturing
- • Design, equipment and supplies
- • Processing and toll manufacturing
- • Sustainability and pollution treatment services
- • Facilities management services
Leather
- • Finished leather good manufacturing
- • Leather goods, Leather Garments manufacturing
- • Next generation Leather Footwear & components.
- • Leather Fashion Accessories manufacturing
- • Leather Tanneries.
Engineering & Process Equipment
- • Engineering solutions segments like chemicals and petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals and automotive for a growing demand for process equipment
- • Next generation automation tools like smart robotics in high precision industries
- • Green Engineering
Chemicals
- • Bio-based raw materials to reduce dependence on oil
- • Chemical based operations &manufacturing
- • Production of fertilizers from Rock phosphate found in Bundelkhand region.
Textiles
- • Raw fabric and dye production
- • Processing & Packaging
- • Spinning, weaving, stitching etc.
Food and Agriculture
- • Processed food, ready to eat packaged food, premixes, milk & dairy, bakery and processed meat
- • Backend infrastructure such as cold chain storage, farm collection center, etc.
- • Health food, health beverages, food additives such as vitamin additives, etc
- • Food packaging, innovative packaging for processed food
- • Contract manufacturing for crop protection chemicals, crop nutrients
- • Poultry, feed and farm additives
Defence Offset
- • New age information systems
- • Communication platforms
- • Simulators and equipment
Ecosystem support &Financing
- • Creation of business facilitation centers with linkage of all stakeholders i.e. Industry Associations, equity funds, banks and financial institutions.
- • Loan Finance
- • Alternate financing sources like securitization of trade credit, securitization of MSME credit, mezzanine financing, access to equity capital through SME Exchanges, Angel Funds / Venture Capital Funds etc.
Skill Development & Tool Rooms
- • Skilling development centres & tool rooms depending on current industrial demand across sectors and districts.